Zucchini vs Pumpkin
Zucchini (Ridge Gourd) – A Highly Beneficial Vegetable for Health!
Zucchini, courgette or Cucurbita pepo var. cylindrica is a summer squash, a vining herbaceous plant whose fruit are harvested when their immature seeds and epicarp are still soft and edible. It is closely related, but not identical, to the marrow; its fruit may be called marrow when mature. Zucchini, containing essential nutrients like potassium and magnesium, offers numerous health benefits.
Zucchini is an extremely beneficial summer vegetable that is consumed in both cooked and raw forms. Packed with multiple health-boosting nutrients, this vegetable holds many advantages.
Some of its benefits include:
Low in calories but rich in vitamin C, potassium, and folate, making it highly beneficial for health.
Zucchini contains lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that protect the body from harmful compounds.
High in water and fiber, it helps maintain good digestion.
The fiber in zucchini prevents sudden spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
The potassium and magnesium in this vegetable help control blood pressure and promote better heart health.
The lutein and beta-carotene found in zucchini are beneficial for the eyes, reducing the risk of age-related vision problems.
Being rich in fiber and water, zucchini gives a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight loss.
It contains a good amount of manganese, vitamin K, and magnesium, which help strengthen bones.
The Blessing of Summer: 8 Amazing Health Benefits of Zucchini Gourd
Zucchini gourd (turai) is a soft and light vegetable that is mostly available during the summer season.
Not only is it delicious in taste, but it is also extremely beneficial for health. Consuming zucchini gourd provides the following incredible and unique benefits:
What are the Benefits of Eating Zucchini?

8 Outstanding Benefits of Eating Zucchini Gourd
1. Kidney Cleansing
Zucchini gourd is naturally rich in fiber and water, which helps flush out toxins from the body and effectively aids in cleansing the kidneys through urination.
2. Eye Protection
Zucchini gourd contains nutrients like lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect the eyes from light-induced damage and improve vision.
3. Aids in Faster Wound Healing
Zucchini gourd contains essential nutrients like vitamin C and zinc, which help in quick wound healing and skin repair.
4. Improves Digestive System
Zucchini gourd has a good amount of fiber, which cleanses the intestines, relieves constipation, and keeps the stomach light. It keeps the digestive system active and improves its function.
5. Enhances Skin Glow
The antioxidants and vitamin C present in zucchini gourd keep the skin fresh, prevent wrinkles, and provide a natural glow to the face.
6. Promotes Heart Health
Zucchini gourd is rich in potassium, magnesium, and fiber, which help maintain balanced blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart diseases.
7. Beneficial for Liver
Consuming rucchini gourd reduces liver inflammation and helps detoxify it. It is a light, safe, and beneficial food for people suffering from liver diseases.
8. Good for Diabetic Patients
Zucchini gourd is low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which helps control blood sugar levels and prevents sudden spikes in glucose levels.
What are 5 Benefits of Eating Pumpkin?

Health Benefits of Pumpkin:
Pumpkin is counted among those vegetables that can be called a priceless gift from nature. Pumpkin belongs to a great family of fruits and vegetables known as Cucurbitaceae, which includes squash, bottle gourd, ridge gourd, sponge gourd, cucumber, bitter gourd, melon, watermelon, and others. The botanical name of pumpkin is Cucurbita pepo.
The Holy Quran also mentions this family of vegetables by the name “Yaqteen.” Pumpkin was also a favorite food of our beloved Prophet Muhammad (PBUH).
Types of Pumpkin
Generally, there are five types of pumpkin: sweet pumpkin (halwa kaddu), round pumpkin, bottle gourd (ghia kaddu), red pumpkin, and white bitter pumpkin. Their benefits are more or less similar.
They contain nutrients that promote muscle growth, along with abundant fatty and mineral salts, making it an extremely powerful vegetable.
Every part of the pumpkin, from its stem to its seeds, is beneficial. Pumpkin seed oil has been used by ancient physicians for years to treat brain dryness, high blood pressure, and nerve tension. While people take sleep-inducing medicines, perhaps nothing is better than pumpkin seed oil for deep sleep.
Chemical Components Found in Pumpkin
Nature has packed pumpkin with many beneficial nutrients. It contains calcium, potassium, zinc, and iron in abundance, along with vitamins A and B-complex. It also contains phosphorus,
Zucchini vs Pumpkin: A Comprehensive Comparison

Zucchini and pumpkin are both members of the Cucurbita genus, commonly known as the gourd family. While they share a similar botanical background and some nutritional qualities, they have distinct differences in their appearance, culinary uses, and flavors.
Appearance and Classification
- Zucchini: Zucchini is a type of summer squash, typically harvested when the skin is tender and the seeds are still soft. It is usually long, cylindrical, and has a dark green or yellow skin.
- Pumpkin: Pumpkin is a type of winter squash, characterized by its hard, thick outer rind. While we often think of pumpkins as large and round, they can come in various shapes and sizes.
Culinary Uses
- Zucchini: Zucchini has a mild, delicate flavor and can be eaten raw or cooked. It is often used in savory dishes like stir-fries, gratins, and as a pasta substitute (“zoodles”). It is also used in baked goods like zucchini bread.
- Pumpkin: Pumpkin has a sweeter, more robust flavor. It is most often cooked and used in both sweet and savory dishes, such as soups, pies, breads, and roasted vegetable sides. The seeds are also a popular snack.
Nutritional Highlights
Both zucchini and pumpkin are low in calories and rich in nutrients, but they have some key differences in their nutritional profiles.
- Zucchini: A good source of potassium and manganese.
- Pumpkin: An excellent source of beta-carotene, which the body converts to Vitamin A, and also contains high amounts of Vitamin C, potassium, and fiber.
1. Botanical Classification and Origin
Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo, Cucurbita maxima, Cucurbita moschata)
Family: Cucurbitaceae (gourd family)
Origin: Native to North America, with evidence of cultivation dating back over 7,000 years.
Varieties: Includes sugar pumpkins, giant pumpkins (C. maxima), and butternut squash (C. moschata).
Growth Habit: Vine-based, requiring ample space to spread.
Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo)
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Developed in Italy in the 19th century from New World squash.
Varieties: Includes green, yellow, and striped varieties.
Growth Habit: Bush-type plant, more compact than pumpkins.
Key Difference: While both are part of the same family, pumpkins are typically larger and vine-grown, whereas zucchini is a type of summer squash with a bushy growth habit.
2. Appearance and Physical Characteristics
Pumpkin
Shape: Round or oblong, with deep ribbing.
Size: Ranges from small (2-5 lbs) to giant (over 100 lbs).
Color: Typically orange, but can be white, green, or blue-gray.
Skin: Thick, hard, and often grooved.
Flesh: Thick, dense, and fibrous, with a central seed cavity.
Zucchini
Shape: Cylindrical, slightly tapered.
Size: Usually 6-8 inches long when harvested young (can grow much larger).
Color: Dark green (most common), yellow, or light green with stripes.
Skin: Thin, tender, and edible.
Flesh: Soft, moist, with small, edible seeds.
Key Difference: Pumpkins are larger with thick skin, while zucchini is slender with tender, edible skin.
3. Flavor and Texture
Pumpkin
Flavor: Sweet, earthy, and slightly nutty when cooked.
Raw Taste: Bland and starchy.
Texture: Becomes creamy and smooth when cooked.
Zucchini
Flavor: Mild, slightly sweet, with a subtle grassy note.
Raw Taste: Crisp and refreshing.
Texture: Tender and slightly crunchy when raw; softens when cooked.
Key Difference: Pumpkin is sweeter and starchier, while zucchini is milder and more versatile in raw and cooked dishes.
4. Culinary Uses
Pumpkin
Cooked Dishes: Roasted, pureed for soups, pies, and bread.
Baking: Pumpkin pie, muffins, and pancakes.
Savory Uses: Curries, stews, and risottos.
Seeds: Roasted pumpkin seeds (pepitas) are a popular snack.
Zucchini
Raw: Sliced in salads, spiralized into “zoodles.”
Cooked: Grilled, sautéed, stir-fried, or baked in casseroles.
Baking: Zucchini bread, muffins, and fritters.
Stuffed: Hollowed and filled with cheese, meat, or grains.
Key Difference: Pumpkin is mostly used cooked, while zucchini is eaten both raw and cooked.
5. Nutritional Comparison (Per 100g Raw)
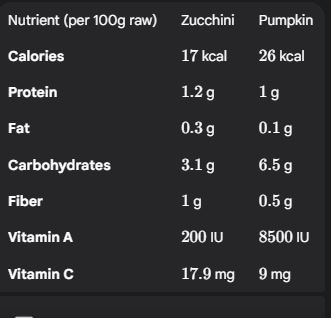
Pumpkin is richer in Vitamin A (beta-carotene), supporting eye health.
Zucchini has fewer calories, more fiber, and higher Vitamin C.
Both are low-calorie, hydrating, and nutrient-dense.
6. Health Benefits
Pumpkin Benefits
Boosts Immunity: High in Vitamin A and C.
Supports Vision: Beta-carotene converts to Vitamin A.
Heart Health: Potassium helps regulate blood pressure.
Digestion: Contains fiber (more when cooked).
Zucchini Benefits
Weight Loss: Low-calorie, high-water content.
Hydration: Over 95% water.
Antioxidants: Lutein and zeaxanthin for eye health.
Blood Sugar Control: Low glycemic index.
Key Difference: Pumpkin excels in Vitamin A, while zucchini is better for hydration and weight management.
7. Growing Conditions
Pumpkin
Season: Warm-season crop, harvested in fall.
Soil: Rich, well-drained, pH 6.0-6.8.
Space: Needs 50-100 sq ft per plant (vining habit).
Time to Harvest: 90-120 days.
Zucchini
Season: Summer squash, harvested young.
Soil: Fertile, moist, pH 6.0-7.5.
Space: Bush variety needs ~9 sq ft per plant.
Time to Harvest: 40-60 days.
Key Difference: Pumpkins take longer to grow and need more space, while zucchini is fast-growing and compact.
8. Storage and Shelf Life
Pumpkin: Whole pumpkins last 2-3 months in cool, dry places. Once cut, refrigerate for 5-7 days.
Zucchini: Best used fresh; lasts 1-2 weeks in the fridge.
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
Pumpkin if you want a sweet, hearty vegetable for baking, soups, or roasting.
Zucchini if you prefer a mild, versatile veggie for salads, stir-fries, or low-carb dishes.
Both are nutritious, delicious, and easy to grow, making them excellent additions to any diet. Whether you’re making a pumpkin spice latte or a zucchini noodle stir-fry, each brings unique flavors and benefits to the table.

